Today’s Discrete Manufacturing companies face a constant challenge of improving operational efficiency and maximising profitability. One crucial aspect that plays a significant role in achieving these goals is effective Cost Accounting. By implementing cost accounting practices, businesses can gain valuable insights into their Production Costs, make informed decisions, and drive growth.
Let’s explore the benefits of cost accounting and how it can revolutionize your business.

What is Cost Accounting Meaning?
Cost accounting meaning is a specialized branch of accounting that focuses on the analysis, measurement, and control of costs within a company. It involves tracking and allocating costs to different activities, products, or services, providing valuable information for decision-making, budgeting, and pricing strategies. Cost accounting helps manufacturing businesses understand the true cost of production, enabling them to identify areas for cost reduction, improve efficiency, and optimize profitability.
What are the Objectives of Cost Accounting?
Cost Determination
One of the primary objectives of cost accounting is to accurately determine the cost of producing goods or providing services. This involves analyzing various cost components such as materials, labor, overhead, and other expenses.Example: In a manufacturing company, cost accounting helps determine the total cost of producing a unit of a product by considering direct material costs, direct labor costs, and manufacturing overhead.
Cost Control
Cost accounting aims to control and manage costs to ensure efficient use of resources. It involves identifying areas of unnecessary expenditure and implementing measures to reduce costs.Example: By analyzing the cost of raw materials and identifying cheaper suppliers without compromising quality, a company can effectively control its production costs.
Cost Analysis
Cost accounting enables detailed analysis of costs by segment, department, product, or activity. This analysis helps in identifying profitable and unprofitable areas of business.Example: Cost analysis might reveal that certain product lines are generating higher profits than others, allowing the company to allocate resources more strategically.
Pricing Decisions
Cost accounting assists in setting appropriate prices for products or services by considering production costs, market demand, and competitive pricing strategies.Example: Using cost data, a company can determine a suitable pricing strategy that covers costs while remaining competitive in the market.
Performance Evaluation
Cost accounting aids in evaluating the performance of departments, products, or projects by comparing actual costs against budgeted costs.Example: A department’s performance can be assessed by comparing its actual expenses with the budgeted expenses to identify areas where cost control measures are needed.
Decision Making
Cost accounting provides relevant information for making informed business decisions, such as whether to make or buy a component, invest in new equipment, or discontinue a product line.Example: Through cost analysis, a company can decide whether it’s more cost-effective to manufacture a component in-house or purchase it from an external supplier.
What is a Cost Concept in Accounting? How it impacts?
A Cost Concept refers to the various ways costs are classified and allocated in accounting. Different cost concepts impact how costs are recognized, measured, and assigned within an organization.
Historical Cost Concept
This concept records assets and liabilities at their original acquisition cost. It’s used for financial reporting purposes and provides a reliable, verifiable basis for valuing assets.Example: A piece of machinery purchased for $10,000 is recorded on the balance sheet at its original cost, even if its market value has increased over time.
Opportunity Cost Concept
This concept considers the potential value of the next best alternative forgone when a decision is made. It’s often used in decision-making scenarios to assess the cost of choosing one option over another.Example: If a company decides to allocate resources to project A instead of project B, the opportunity cost is the potential benefits that project B would have provided.
Sunk Cost Concept
Sunk costs are past expenses that cannot be changed by future actions. These costs should not influence decision making, as they are irrelevant to future costs and benefits.Example: If a company invests $100,000 in a project that is no longer viable, the sunk cost should not be considered when deciding whether to continue the project.
Fixed and Variable Cost Concepts
Costs are categorized into fixed costs (remain constant regardless of production levels) and variable costs (change with production levels). Understanding these concepts is vital for break-even analysis and cost-volume-profit analysis.Example: Rent is a fixed cost, while raw materials are a variable cost. The company’s total rent remains the same whether it produces 100 units or 1,000 units.
Direct and Indirect Cost Concepts
Direct costs can be traced directly to a specific cost object (e.g., a product), while indirect costs cannot be easily traced to a single cost object and require allocation methods.Example: In a bakery, the cost of flour used to make a specific type of bread is a direct cost, while the cost of the electricity used to power the ovens is an indirect cost.
The choice of cost concepts impacts how costs are accounted for, evaluated, and used for decision making within an organization. Different contexts and decision scenarios may call for the application of specific cost concepts to provide relevant and accurate information.
What is the Importance of Cost Management Accounting in Companies?
Cost Management Accounting plays a crucial role in manufacturing companies by offering several key benefits. It helps many manufacturing companies to arrive at the Product Costs and what elements contributed to the same. By identifying the not needed process or any other cost cutting measures will reduce Product Costs and helps the Company profits.
a. Accurate Cost Determination
Cost accounting provides accurate cost information, enabling businesses to calculate the cost of each product or service. This information is essential for pricing decisions, inventory valuation, and profitability analysis.
b. Cost Control and Reduction
By analyzing the various cost components, businesses can identify areas of inefficiency and take corrective actions. Cost accounting helps control costs by highlighting wasteful processes, minimizing overhead expenses, and optimizing resource utilization.
c. Decision-making Support
Cost accounting provides valuable insights into the financial impact of different production choices. It helps managers make informed decisions regarding product mix, pricing, outsourcing, or in-house production, leading to improved profitability.
d. Performance Evaluation
Cost accounting facilitates the evaluation of departmental or product-wise performance. By comparing actual costs against budgeted costs, businesses can identify areas of improvement and take proactive measures.
What are the Elements of Cost Accounting?
Cost accounting involves several key elements that contribute to a comprehensive understanding of costs:
- Direct Materials: The cost of raw materials used in the production process.
- Direct Labor: The cost of labor directly involved in manufacturing activities.
- Manufacturing Overhead: Indirect costs such as utilities, maintenance, depreciation, and supervision.
- Indirect Materials and Labor: Costs incurred indirectly in the production process.
- Selling and Administrative Expenses: Costs associated with selling products or services and general administrative functions.
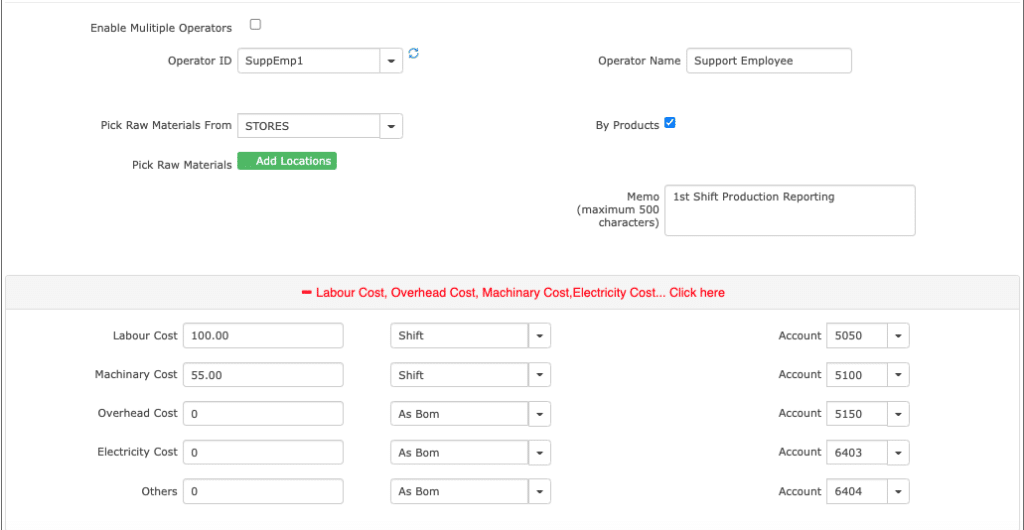
Few of these costs are added as part of FG Reporting. For example Direct Labor, Direct Machine costs and the additional OH costs are added as part of Production Reporting.
Types of Cost Accounting
Cost accounting is a specialized branch of accounting that focuses on the analysis and measurement of costs within an organisation. It provides valuable information for decision-making, cost control, and performance evaluation. Within cost accounting, there are different types of costing methods used to track and allocate costs. Let’s explore some common types of cost accounting:
Job Order Costing
Job order costing is used when products or services are produced on a customized or unique basis. It involves tracking costs for each specific job or project. Costs are allocated to individual jobs based on the direct materials, direct labor, and overhead expenses associated with that job. This method is commonly used in industries such as construction, custom manufacturing, and professional services.
Process Costing
Process costing is employed when products or services are produced in a continuous or repetitive manner. It involves allocating costs to each production process or department. The total costs are spread out over the units produced, resulting in an average cost per unit. This method is commonly used in industries such as food processing, chemical manufacturing, and mass production.
Activity-Based Costing (ABC)
Activity-Based Costing is a method that focuses on identifying and allocating costs based on the activities that drive those costs. It involves analyzing the various activities performed within an organization and assigning costs to specific cost drivers. By linking costs to activities, ABC provides more accurate insights into the cost of products, services, or processes. This method is particularly useful when overhead costs are significant and when there is a diverse range of products or services.
Note:
ACTouch ERP Follows this ABC model for cost accounting. We found that ABC Costing is a good model for Process industry where the production models are constant. In case a frequent changes in Production reporting or Purchase etc which has a direct impact on the product costs, ABC is not a good model. Discuss with our ERP Consultant.
Standard Costing
Standard costing involves establishing predetermined standards for various cost elements, such as materials, labor, and overhead. These standards serve as benchmarks against which actual costs are compared. Variances between standard costs and actual costs are analyzed to identify inefficiencies, deviations, and areas for improvement. Standard costing provides a basis for cost control and performance evaluation.
Marginal Costing
Marginal costing, also known as variable costing, focuses on analyzing the behavior of costs and their impact on profitability. It separates costs into fixed costs and variable costs. Variable costs, which vary with the level of production or activity, are directly attributed to each unit produced. Fixed costs are considered period costs and are not allocated to individual units. Marginal costing helps in understanding the contribution margin and making decisions related to pricing, product mix, and break-even analysis.
Lean Accounting
Lean accounting is a cost accounting approach that aligns with lean manufacturing principles. It aims to eliminate waste and improve efficiency in all aspects of the business, including accounting processes. Lean accounting focuses on providing relevant and timely financial information to support decision-making within a lean organization. It emphasizes simplicity, value stream costing, and performance measurement based on lean metrics.
These are just a few examples of the types of cost accounting methods used in various industries. Each method has its own advantages and is applicable in different contexts. Organizations choose the most appropriate cost accounting method based on their industry, production processes, and management objectives. Effective cost accounting enables businesses to accurately measure costs, make informed decisions, and optimize their resources for improved profitability and sustainability.
Difference between Cost Accounting vs. Financial Accounting:
While cost accounting and financial accounting share similarities, they serve different purposes:
Cost Accounting:
- Focuses on internal reporting for management decision-making.
- Emphasizes the analysis of costs and cost behavior.
- Provides detailed information about product, process, or activity costs.
- Aims to control and reduce costs within the organization.
Financial Accounting:
- Focuses on external reporting for stakeholders and regulatory compliance.
- Emphasizes the preparation of financial statements.
- Provides an overview of the organization’s financial position, performance, and cash flows.
- Aims to ensure transparency and accountability to external parties.
Difference between Cost Accounting and Management Accounting:
Cost accounting and management accounting are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct characteristics as below.
Cost Accounting:
- Focuses on the measurement and control of costs.
- Provides detailed information on product costs and cost drivers.
- Aims to optimize costs and improve profitability.
Management Accounting:
- Focuses on providing information for internal decision-making.
- Provides broader financial and non-financial information for planning, control, and performance evaluation.
- Aims to support strategic decision-making and overall organizational management.
What do You Mean by Cost Sheet?
A cost sheet is a document prepared by cost accountants that summarizes the costs incurred in the production process. It includes detailed information about direct materials, direct labor, manufacturing overhead, and other relevant costs. The cost sheet acts as a valuable reference for calculating the total cost per unit and determining the selling price of a product.
Conclusion: Implementing cost accounting practices in your manufacturing business is vital for staying competitive and maximizing profitability. ACTouch Cloud ERP Software offers robust cost accounting capabilities that enable you to gain insights into your production costs, make informed decisions, and enhance your overall operational efficiency. By leveraging the benefits of cost accounting, you can optimize your manufacturing processes, control costs, and drive sustainable growth. Embrace the power of cost accounting with ACTouch Cloud ERP Software and take your manufacturing business to new heights of success.