One of the biggest issues faced by Customer after purchase of ERP License is to Implement an ERP Software as per their needs in their Company. So ERP implementation Cycle consists of multiple stages and Enterprise Resource Planning Software implementation takes time and is not a day’s job. It requires Data Analysis, Planning, Preparation, Users Testing, Accepting the changes and Go Live. Considering the various dimensions of manufacturing Units, it clearly optimises the efficiency of managing your business and also largely contributes to the profitability of your business.
In summary, ERP Implementation cycle consists of lot of preparation work than follow the process.
Cheatsheet1 – How to prepare the Core Team and what they should do?
- Identify the Core team, who implements ERP Software – One problem we always found here is, customer put their best employees as part of “Core Team”. But the capability of this team is different from the rest or normal teams. So be careful on what you want. Identify the human resources with a focus on successful implementations of an ERP Software. Identify a separate project team for implementation phase that may have different skillsets.
- Write down your current business processes from design phases – Many companies fail in ERP implementation, not because they are not good. But during Cloud-based ERP implementation cycle, they identify many features that ERP has. Now they FEEL, it may help and not thinking twice they want to implement. But in reality, no one in the company uses or they are not equipped to handle that process. So identifying a project team with a good Project Manager is important.
- Ensure that management representative is the head of Team and he is FREE – Yes, he should be FREE and available during the complete ERP implementation lifecycle. He should own the project plan with a careful planning of resource and also ensure that daily operations in factory happens too. So its a crucial step.
- Time is money – More you are prepared, more you are lucky. If needed identify an implementation partner who has an actual implementation experience too. He should know different implementation stages, it’s nuances, potential issues and how to manage key phases with project team.
- Take Quick Decision, rather wait on the same during Implementation lifecycle.
- Keep a separate Implementation team / project team that’s FREE from their regular works. Identify the legacy systems, what would be project costs, what are the business functions and its functional requirements to be migrated etc.
- Detailed training phase with cost of ownership with an idea on what kind of testing to be done like stress testing or extensive testing or a simple unit testing etc. A detailed design can help with a good end-user training and its delivery too.
Understand more on ERP Implementation Cycle
Stage 1: ERP Software and the ERP Vendor SELECTION
Each and every business today has different requirements and totally different modifications for the business to function smoothly. There are numerous options available in the market but choosing the right ERP software for your business becomes very essential. Choosing the required ERP modules for your business becomes crucial in deciding how successfully your business runs. So, selection of ERP modules is determined on the functional expectations of various business divisions, such as Finance, Procurement, Warehouse etc. Knowing the list of business requirements based on business activities or new business strategy can help with defining a good implementation plan with a clearly defined process of implementation.
The selection of an ERP package for your business may depend on the following criteria:
Functionality fit for your organisation – How your business performs, what functionality that you want to bring into ERP and the appropriate ERP modules for that functionality of your business determines the ERP software compatibility with your business.
Price – Today’s business world has become excessively price competitive in the market. So whenever a business is selecting an ERP package it has to take into consideration the Return on Investment (ROI).
However PRICE is not the only factor.
Old adage is “If you throw the peanuts, you get Monkey’s”
Select the Right ERP Software vendor – Here the business has to know about the size of the customer base of the vendor. Knowing the size of the customer base and financial status of the software company can give a fair idea on how viable is the software vendor. Important is, whether this vendor understands your business and its practices?
Risk – Usually risk is involved in all business transactions today and eventually the software that your organisation opts for also might not be completely risk free. Taking the time to create a thorough map of the key business processes that are essential for the operations of your organisation and using that throughout the ERP selection and implementation might negate risk to a great extent.
Scalability of ERP Software as the Business grows – Always while evaluating an ERP, we should consider how the technology fits with your business operations and strategies today and down the road.
Read more about ERP Vendor Selection A cheatsheet designed for ERP Novices.
Stage 2: Project Planning
Planning is very crucial before kicking off any project so that you are not caught off guard with surprises during the implementation. ERP implementation cannot be achieved with allocating the right resources to the required task to the appropriate team member, so planning is the key for right ERP implementation.
Stage 3: Gap Analysis / Current System Study
This is the stage of project review to identify, “How Organisations determine to achieve their business goals and compare them with their current state”. Here the focus is to have an ideal goal state that determines how effectively the Company can know the shortcomings and opportunities for its improvement.
ERP vendors can do a GAP Analysis and can suggest to do few customisation to meet your current practices or better follow the Right ERP and change the process.
This is an important step in ERP Implementation process.
Stage 4: Remodelling
To make the business process more efficient remodelling of the alterations and changes based on planning and gap analysis has to be made.
This stage process is decided mainly due to below reasons.
- Additional Features available in ERP and stakeholders wants to use them
- Management decided to change their business focus and decided to automate few process.
- Existing process could be simplified due to this new ERP process. Save of money and man power.
Note- Many customers dont want to rework or redo their process as they are afraid of missing something. So they prefer to have an ERP that’s used in their competitors place.
Assumption is “If an ERP works in my XYZ Competitor, it should work for us too”.
Many customers avoid to analyse their STRENGTHS and what they should do.
Stage 5: Training of Employees
There is always a requirement for training the employees with handling the ERP software that the business has adopted for smooth manoeuvring of its daily business operations. End-users are trained to use ERP system efficiently so that benefits from the system are obtained.
Stage 6: End USER Acceptance Testing (UAT)
The testing phases in ERP Implementation Life Cycle is usually done to assess the errors and to take corrective measures to resolve before actually implementing the ERP software.
Stage 7: ERP System Application
In this stage of the life cycle the ERP system is up and running. All the data that is collated is analysed and fed into the system, where the older system is discarded. The users of the ERP system and the technical support resources must continue to validate and verify proper operation of the ERP system.
Stage 8: ERP Maintenance
This is the final stage in the ERP Implementation Life Cycle. Here the responsibility of the employees kick in to stay updated with latest technology the market offers and to keep the system up and running.
How, ACTouch follows a Cloud ERP Implementation cycle with controls?
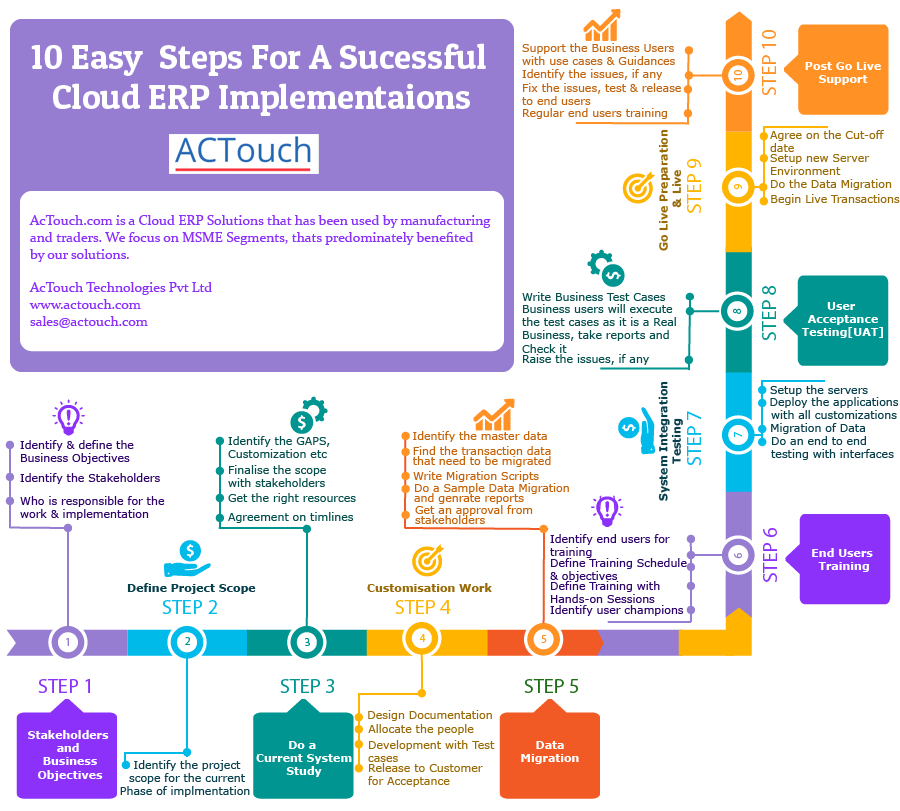
We follow an international ERP implementation practices thats been fine tuned based on customer feedback and our experiences. Below are the 10 steps that we follow to make our customers projects are successful.
To provide a complete business solutions, ACTouch cloud ERP integrated with eInvoice features provided by TCS iON. Now our customer has an end to end solutions.
Steps to follow an ERP Implementation Cycle and its process.
Step 1: Define Stake Holders and Business Objectives
- We mainly identify what are the business objectives and accordingly define them to suit the business.
- Then we identify and documenting all the stakeholders on the project, including their interests, impact, and potential negative influences on the project.
- And finally determine who is responsible for the work and implementation of the software.
Step 2: Define Project Scope
- We identify the prospective customers’ project scope and their utilities.
- What functionality is required by end user for running their business efficiently will be defined here and accordingly serviced.
Step 3: Do A Current System Study
- Identification of GAPS for the particular business is done and appropriate customizations are executed.
- Analysis of the current system on which the business is run and getting the right resources for improving the business is made.
- The agreement on timeline planning and implementing the ERP software is finalised with the business owner.
- And the scope and the functionalities of the ERP software is finalised with the stakeholders.
Step 4: Customisation Work
- Designing the documentation for alterations and changes is done.
- We allocate the right people for making the essential documentation related changes and alterations for the particular business.
- The manual tests are run on the ERP software for error detection and for customisation of the software according to needs of the customer.
- Then the ERP software is then released to the customer for acceptance.
Step 5: Data Migration
- Here the master data is collated and the transaction data that has to be migrated from the existing software to the new ERP software is found.
- The back end scripts are written for any new updations or changes in the business model.
- Then a sample data migration is done, sample reports are generated and approvals from the stake holders are taken for further processing.
Step 6: End Users Training
- The end users of the ERP software are identified and the necessary training is given to operate on the software.
- The training objectives are defined and the scheduling for the training is prepared.
Step 7: System Integration Testing
- Separate server is setup on demand from the customer for the existing database.
- Next the deployment of the applications such as inventory management, procurement etc., are executed and the required customizations of the applications as required for the business in done.
- Migration of the data and end to end testing with the user interfaces is completed.
Step 8: User Acceptance Testing (UAT)
- The test cases for the business are written.
- Then the business users will execute these test cases assuming it as a real business.
- The report that is generated on running the test cases are checked and if any issues are found then it is appropriately raised for correction.
Step 9: GO LIVE preparation and Go live.
- A specific date for the ERP software to go live is approved.
- Setting up of new server for managing all databases is done.
- The data is migrated from old software to new ERP software.
- The real world business transaction on the ERP software has commenced.
Step 10: Post GO LIVE Support
- The business users are supported with use cases.
- Guidance regarding the use cases are provided and any issues related to the software are rectified, tested and released to the end user.
- Regular end users training are provided for any updations in the ERP system.