Here we are trying to address the below questions related to Routing Process.
- What is Routing?
- What is purpose of Routing process?
- How Routing process helps?
- Whats the basic Routing technique?
What is Routing Process? How to create it?
Routing ID helps to create the steps to follow to manufacture a Finished Goods. This predefines the steps to follow and what items to produce at each stage with BOM to be used etc.
A single Product can multiple ROUTING IDs. Based on the type, you can define and select the Products in the Work Order.
Definition of Routing and example to explain more
In the context of manufacturing, a “routing definition” refers to a detailed plan or sequence of operations that outlines how a product will be produced from start to finish. It is a crucial aspect of the manufacturing process as it provides step-by-step instructions for the transformation of raw materials into a final product.
The Routing Definition typically includes the following elements:
- Operations: The list of all the manufacturing steps required to produce the product. These operations could include cutting, welding, drilling, assembly, painting, testing, and more.
- Workstations / Work Centers: The specific locations or work areas where each operation will be carried out. Different workstations may have specialized equipment and tools suited for particular tasks.
- Operation Sequence: The order in which the operations need to be performed. It ensures that the manufacturing process flows smoothly and efficiently.
- Time and Resources: The estimated time required to complete each operation and the resources (raw materials, machinery, labor, etc.) needed for each step.
- Quality Checks and Inspection Points: Specific points in the process where quality checks or inspections are performed to ensure that the product meets the required standards.
Example:
Let’s consider the manufacturing of a simple wooden chair. The routing definition for this product might look like this:
- Operation: Cutting the wooden pieces for the chair.
- Workstation: Sawing station
- Time: 30 minutes
- Resources: Wooden planks, saw machine, worker
- Operation: Shaping and sanding the chair parts.
- Workstation: Shaping and sanding station
- Time: 45 minutes
- Resources: Shaping and sanding tools, worker
- Operation: Assembling the chair.
- Workstation: Assembly area
- Time: 20 minutes
- Resources: Wooden pieces, screws/nails, worker
- Operation: Applying a finishing coat.
- Workstation: Painting booth
- Time: 15 minutes
- Resources: Paint, painting equipment, worker
- Operation: Quality inspection and packaging.
- Workstation: Quality control area
- Time: 10 minutes
- Resources: Inspection tools, packaging materials, worker
The routing definition ensures that the chair manufacturing process follows a systematic approach, and each step is clearly defined with allocated time and resources. This helps in streamlining the production process, optimizing resource utilization, and ensuring the quality and consistency of the final product.
Routing Process Details
Steps to follow is as below.
- Define a ROUTING ID
- Attach the same to Product Master. As Planning module will consider the ROUTING to follow when we create the Work Orders.
- When you create the Work Orders manually, select the ROUTING that suits for that WORK ORDER and for that FG.
- Based on the ROUTING ID, these process are added to the Work Order. You can still delete few of these Process steps and add your own too.
Before we begin the work on / defining the Process steps, below are the mandatory data required.
- Product ID
- Operations ID
- Work Centre – This should be connected with Operations and FG products that manufactured at that place.
- Tools ID
- Need to have an idea on each PROCESS and whether its done in IN HOUSE or SUBCONTRACTOR place?
There are few fields that are very important to understand and how to use them?
- Move to FG ID / WIP to next Operation = YES / NO – Helps to avoid putting the materals request to STORES and receive the materials.
- Maintain Stock – Most of the cases, we keep the physical inventory of Produced items. In few cases, we report production and efforts, but don’t want to keep the items in “fluid” state. So we use this design.
- Subcontract Operations – Helps to identify the Subcontract operations and enabled “ODC” menu in Work Order screen.
Layout is as below.
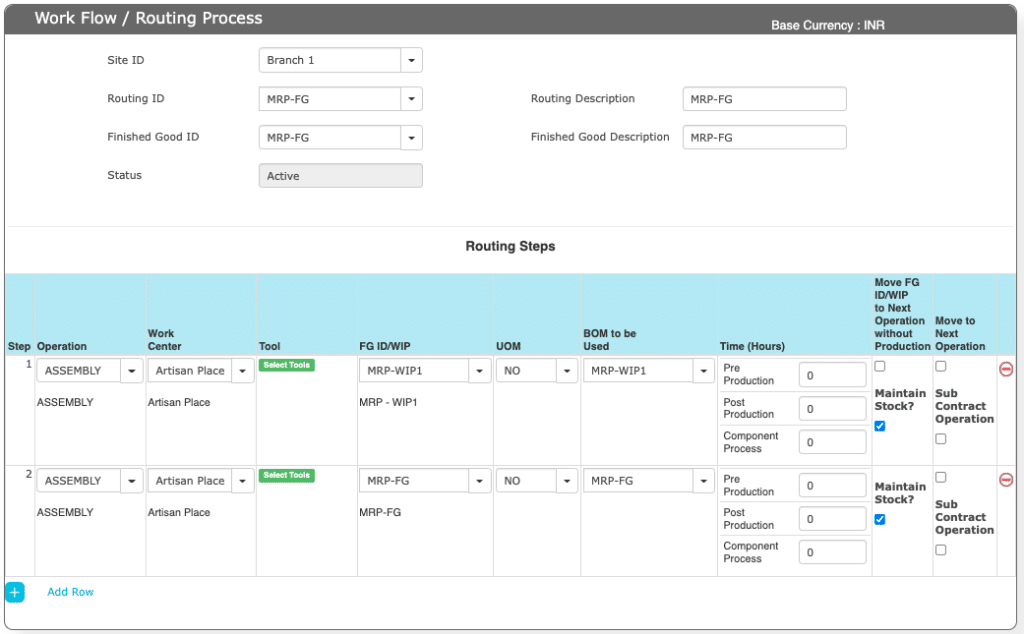
Field details are as below.
| No | Field ID | Field name | mandatory | Field description and how it helps? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Routing ID | Routing Identification Number | Yes | Each step of the working process is identified by using a Unique Routing identification number in the work flow process. Good practice is to have the FG / Semi FG name as ROUTING ID. |
| 2. | Routing Description | Routing Process Description | Yes | The description of the Routing process. |
| 3. | Finished goods ID | Finished goods ID | Yes | FG / Semi FG that’s produced as part of this Routing Steps. |
| 4. | Finished goods Description | Finished Goods description | Yes | FG Name / product description. |
| 5. | Status | Status of the work flow process | Yes | It tells us about the Routing ID is ACTIVE or INACTIVE |
| 6. | Step | Particular step in the routing process. | Yes | It tell us in which step of workflow /routing process we are exactly in. |
| 7. | Operation ID | Operation identification number | Yes | It is the unique identification number given to identify different operations in the work centre. |
| 8. | Work Centre ID | Work Centre Identification Number | Yes | Work center ID, where this work Happens. |
| 9. | Tools ID | Tools Identification Number | No | It gives unique number to identify the appropriate tool which is being used for an operational activity. |
| 10. | Finished Goods ID/WIP | FG ID | Yes | Finished Goods / WIP items that are produced in this step. |
| 11. | UOM | Unit of measurement | Yes | Units of measurement. |
| 12. | BOM to be Used | Bill Of Material | Yes | It gives us which BOM is to be used to the particular Finished Goods production. |
| 13. | Time (Hrs) | Time required for producing the Finished Good | No | Its gives us the total time required for producing the Finished Good. It gives the operational time consumed for producing the Finished Good. |
| 14 | Move FG ID / WIP | Maintain Stock | No | It is always important to keep the Stock of the items that are produced. If it’s “Yes”, the stock is maintained and you need to enter FG ID and BOM related to the same. In Few cases, customer wants to capture the process and efforts, but not the physical stocks. Then set “NO”. |
| 15 | Move to Next Operation | Transfer to next Operational step | No | Normally, when a Semi FG is produced its sent to STORES DEPARTMENT and then we again receive it through MATERIAL REQUEST FORM (MRF) process. In case, you want this Semi FG to move to next Operation automatically, then select this. |
| 16 | Subcontract Operation | Set the value to Yes / NO | No | In case, you want to send this stage RMs to subcontractor to assemble and send back, the enable this flag = YES. Else keep it as it is. |